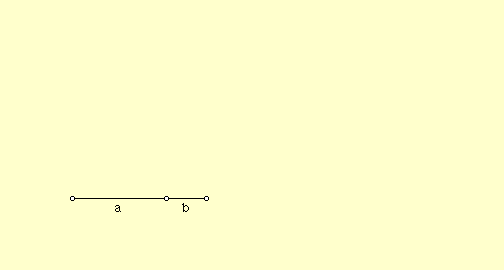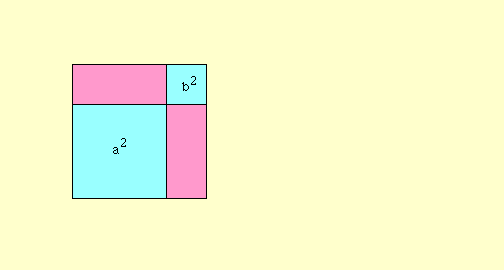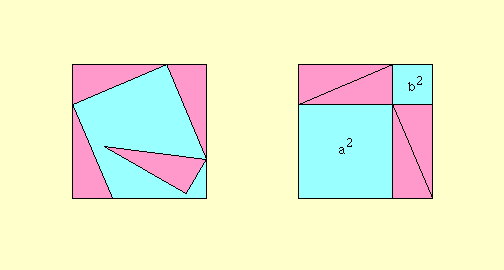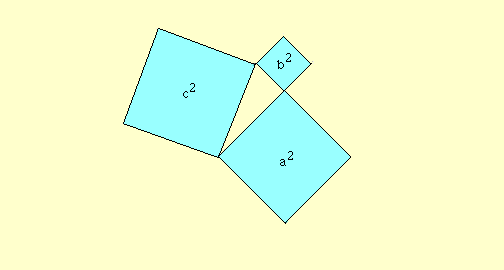
The Pythagorean theorem, named for Pythagoras of Samos (c. 580 B.C - 500 B.C.), was known to the Babylonians one thousand years earlier. It states that if the side opposite the right angle in a right triangle (the hypotenuse) has length c and the other sides of the right triangle have lenghts a and b, then a^2 + b^2 = c^2.
Last updated, Jan. 29, 2008
Tom.Richmond@WKU.edu