Computer Animation - Career Path
Animation
Computer animation
Computer animators
Education and requirements
skills and responsibilities
Career outlook
Animation as an artform
Process and Workflow
Student animations
Animation at WKU
- Animation

- Animation is the rapid display of a sequence of static images that creates the illusion of movement.
- Traditional animation
- (Cut-Out animation, Stop motion animation, Cel animation, etc) is an animation technique in which each frame is drawn by hand.

- Computer animation

- Computer animation, begun in the 1960s, is the art of creating animation, visual effects and other 3D images using computers and specialized software.
- Computer animation has distinct advantages for artists:
- it is cheap and fast to make
- the artist is able to control every aspect of the process unlike traditional animation which cannot be viewed until developed.
- it is cheap and fast to make
- 3D Computer animation
- <Toy Story> (1995) is the first feature length film fully modeled and created with the 3D technology.
<Rolln' Safari>
<Rustboy>
<Wildebeest>
- <Toy Story> (1995) is the first feature length film fully modeled and created with the 3D technology.
- Computer animation, begun in the 1960s, is the art of creating animation, visual effects and other 3D images using computers and specialized software.
- Computer animators

- Where do I start?
- It's easier to get into animation today than ever before.
- Although anyone can start animating right now, the art of animation still takes time to master.
- You can start small and simple and slowly develop your skills and unique style.
- You don't even need to know how to draw well.
- It's easier to get into animation today than ever before.
- What does an animator do?
- Animators bring the lifeless to life.
- Animators, also known as multimedia artists, create animation and visual effects for everything from films and video games to television, mobile devices and other forms of media using illustrations and software programs.
- Animators also create graphics and develop storyboards, drawings, and illustrations. They create, plan, and script animated narrative sequences and assist with background design and production coordination.
- Recent advances in animation technology, along with the increased popularity and diversity of devices used to access entertainment have made computer animator one of the most exciting and lucrative career paths for technically-inclined artists.
- Animators bring the lifeless to life.
- Where do animators work?
- This career path is also ideal for those who want to be their own boss; 57% of animators and multimedia artists are self-employed, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
- These professionals often work from home, contracting with film, animation or video game production studios, cartoon networks, advertising agencies, web design/graphic design firms, and mobile technology companies.
- This career path is also ideal for those who want to be their own boss; 57% of animators and multimedia artists are self-employed, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
- Do you have what it takes to be an animator?
- Animation is no easy task.
- Bringing dynamic images to life is an exciting job, but a career in animation isn’t exactly a walk in the park.
- Many animators work long hours, including nights and weekends, to adhere to strict deadlines. But if you’re passionate about animation and determined to succeed, the high-pressure, fast-paced environment shouldn’t faze you one bit.
- Animation is often the combination of understanding mechanics and making them artful.
- Animation is a mixture of art and science. In order to thrive, you must have an artistic eye but also enjoy breaking things down to see how they work.
Never-Ending Man: Hayao Miyazaki
Yuri Norstein
- Animation is no easy task.
- Where do I start?
- Educations and requirements

- Common topics covered in the animation programs include drawing, 2D animation, film and animation history, visual effects (VFX), motion graphics and design, game design, interactive media, and computer programming.
- Today’s employers prefer to hire animators with at least a bachelor’s degree. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), animators, multimedia artists, and graphic designers generally need a bachelor's degree.
- Employers usually prefer portfolio samples, which students normally create while earning their degree.
- In addition to a 4-year degree, many employers look for at least two years’ experience in the industry, and advanced technology skills. Entry-level positions may require only a degree and experience through an internship or other support position.

- Common topics covered in the animation programs include drawing, 2D animation, film and animation history, visual effects (VFX), motion graphics and design, game design, interactive media, and computer programming.
- Skills and responsibilities

- Making animation is fun and playful, while it requires a great deal of attention and focus.
- Becoming skilled in software is important to furthering yourself in the field.
- What types of software do animators use?
- The leading 3D animation software such as Autodesk Maya, 3ds Max, and Adobe After Effects, Premiere, Photoshop, Flash, Illustrator...
- You’ll need to possess the perfect combination of practical skills and software savvy to flourish in this field.
- Can work 50+ hours per week and even pull all-nighters when deadlines are approaching or work is past due.

- The leading 3D animation software such as Autodesk Maya, 3ds Max, and Adobe After Effects, Premiere, Photoshop, Flash, Illustrator...
- Making animation is fun and playful, while it requires a great deal of attention and focus.
- Career outlook

- 3D computer animation is used in a variety of careers in a number of industries, including media and advertising.
- Popular Career Options
- Computer animation can be used by 3D modelers to convert storyboards into 3D content for motion picture studios, as well as Web designers to create online content for advertising agencies.
- Scientific laboratories often use 3D animation to simulate the structure and movement of natural organisms, while the video gaming industry relies on 3D animation to create engaging content.
- Related career paths are also available for engineers who utilize computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D animation software to create 3D models.
- Computer animation can be used by 3D modelers to convert storyboards into 3D content for motion picture studios, as well as Web designers to create online content for advertising agencies.
- Employment outlook and salary information
- The BLS predicts 4% job growth for computer animators from 2018 to 2028.
- The BLS predicts 4% job growth for computer animators from 2018 to 2028.
- What is the job outlook for animators?
- Despite average employment growth, competition for job opportunities in animation will remain strong.
- The Bureau says, “opportunities should be best for those who have a wide range of skills or who specialize in a highly specific type of animation or effect.”
- Despite average employment growth, competition for job opportunities in animation will remain strong.
- How much do animators make?
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports a median annual wage of $99,060 for special effects artists and animators as of May 2023.
- Median Wage: The median annual wage for special effects artists and animators was $99,060 in May 2023.
- Lowest 10%: The lowest 10% earned less than $57,090.
- Highest 10%: The highest 10% earned more than $169,580.
- Job Summary: Special effects artists and animators create images that appear to move and visual effects for various forms of media and entertainment.
- Industry Profile:
- Motion Picture and Video Industries: $100,910
- Software Publishers: $84,150
- Computer Systems Design and Related Services: $73,320
- Advertising, Public Relations, and Related Services: $74,530
- Motion Picture and Video Industries: $100,910
- Other top paying industries for animators are:
- Aerospace Product and Parts Manufacturing
- Motion Picture and Video
- Software Publishers
- Electromedical, and Control Instruments Manufacturing
- Computer Systems Design
- Advertising and Public Relations
- Salaries for popular job roles similar to computer animation
- Computer Animation Instructor:
- Motion Graphics Designer:
- Flash (Adobe Animate) Animator:
- Advertising Animator:
- Web Animator:
- Mobile Animator:
- Video Game Animator:
- Computer Animation Manager:
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports a median annual wage of $99,060 for special effects artists and animators as of May 2023.
- How to find animation jobs?
- Explore Job Boards specifically for animation:
- Animation Mojo:
- Animation Guild Job:
- Animation Career Review:
- Animation World Network (AWN):
- ArtStation:
- General Job Boards:
- CareerBuilder and Indeed.
- CareerBuilder and Indeed.
- Tips for Finding Animation Jobs:
- Network: Attend industry events and connect with professionals in the field.
- Build a strong portfolio: Showcase your skills and experience through a portfolio of your work.
- Be persistent: The animation industry can be competitive, so be prepared to apply for many jobs and stay persistent in your job search.
- Consider entry-level roles: If you're new to the industry, start with entry-level positions to gain experience.
- Explore Job Boards specifically for animation:
- 3D computer animation is used in a variety of careers in a number of industries, including media and advertising.
- Animation as an art form
- The biggest misconception about art is what is considered art and artists.
- The denigrated status of American Studies in the university is largely due to the belief held in many contries that animation is not a 'real' art form because it is too polpular, too commercilized, or too closely associated with 'fandom' or youth audiences to be taken seriously by scholarts. This impression is faulty because there is a wide range if animation that us not commercially - or child-oriented and, in any case, these areas also merit sudy.
- In these days, in order to be an artist, you have to be a painter, musician, a sculptor, a dancer, or something along those lines.
- You are not considered to be an artist, if you are an animator, a 3D modeler, an editor or a VR (virtual reality) designer. This is a weak and limiting definition of art.
- Art is about creating something unique, it’s about expressing your view of the world in a different way.
- Why is animation not widely considered to be an art form?
- When someone animates something they are creating something meaningful and creative. Animation also requires as much 'creativity' as it does technical skills.
- "Long dismissed as merely children's entertainment, only in recent years has there been clear recognition of animation as an art; as a form that encompasses more than the American animated cartoon tradition; as a medium of universal expression embraced across the globe" - Paul Wells
- Art does not have to be limited to the fine arts. Art is anything that comes into existence through someone’s creativity and work. What is considered art should not be limited to the 'classical' arts per se.
- “To him, all good things - trout as well as eternal salvation - came by grace; and grace comes by art; and art does not come easy” - A River Runs Through It.
- Nicolas Brault
- Brandon Morse
- Rebecca Xu
- “To him, all good things - trout as well as eternal salvation - came by grace; and grace comes by art; and art does not come easy” - A River Runs Through It.
- Process and Workflow

- What is an animation pipeline?
- Animation workflow or pipeline is a system consisting of people, hardware, and software aligned to work in a specific sequential order to do pre-determined tasks in a pre-determined time frame, which will lead to a 3D animation product or asset as the final output.
- The final product could be a traditional animation such as a feature film, short film, animated commercial video, television show, game trailer, or video game asset, or it could be something totally different. It’s much like an assembly line for 3D animated video production.
- Animation workflow or pipeline is a system consisting of people, hardware, and software aligned to work in a specific sequential order to do pre-determined tasks in a pre-determined time frame, which will lead to a 3D animation product or asset as the final output.
- Key components of CGI animation pipeline
- 3D animation production pipeline has three main stages: Pre-production Production Post-production.
- Based on organizational considerations, resources, outcomes, and other factors, each segment of the 3D animation industry uses the three stages a little differently, but the main structure remains intact. The specifics of each project’s pipeline may also be slightly different. However, the three main stages remain the same again.
- Pre-production: Pre-production is the research, designing, and planning phase of the entire 3D project, which is split between two teams: The design team creates the idea, story, and designs, and the management team, who writes down the production plan (including budgets, teams, and time frames). The better the pre-production phase is done, the easier the production stage will be.
- Idea Generation: Every great story starts with a brilliant idea. Thus, it is essential for a successful animation to have a solid, well-thought idea.
- The core idea of a 3D animated video can originate from virtually everywhere and everything; a single word, a sentence, a book, colors, smells, sounds, conversations, real-life events, anecdotes, or philosophies. The most important point is for it to have enough potential to ignite a dialogue within yourself or with others. A flawed or impotent idea will lead to a defective story and ruin the entire endeavor.
- 3D animation ideas; where to start? The word “idea” is defined as “a suggestion or plan for doing something”, “an understanding, thought or picture in mind”, and “a purpose or reason for doing something” in the Cambridge dictionary. However, the definition of an idea is slightly different in the 3D animation industry. Generally speaking, a 3D animated video contains numerous ideas in the form of sentences, character design, setting, background, camera placement, colors, lighting, pacing, and so on. The directing team does not come up with ideas out of the blue; they sort through a mass of ideas to find the ones that are capable of fitting into a coherent whole. It is actually a continuous probe in which you don’t know what exactly you’re looking for at first. To come up with creative ideas, 3D animation studios adopt different procedures based on their own considerations: organization, mechanisms, audience, product type, etc. Creative teams usually put their raw ideas or concepts into a strict manufacturing process which will finally develop into a thought-out plan with helpful insights and details, enough to take the project to the next level: Story Creation.
- A good idea for a 3D animation is original and avoids clichés: A worn-out concept, character, symbol, or plot that has lost its originality can degrade your 3D animation idea to a significant extent. Generally speaking, you should avoid clichés but just in case you choose to stick to your clichés anyway, at least you can find a way to make it look fresh.
- It is either “different” or “better” Your idea must be somewhat different from what has been done before. At least, it must offer a degree of improvement. Otherwise, it’s just an okay idea, or even a bad idea you don’t want to stick to.
- Story Creation: Ideas will be developed and improved until the whole story is shaped. This is a basic version of what’s going to happen in the animation, including the characters, conflict, et cetera.
- Script Writing: The script is the formal, written, literary version of the story; including the character movements, environment, time, actions, and dialogues.
- Storyboarding: A storyboard is a non-moving visual version of the script. It basically looks like a comic book, including early ideas of camera staging, major character poses, or scene events.
- Animatic: A moving form of the storyboard is called the animatic which will evolve into the final edit of the entire project. The animatic is created in its most simple form, portraying the sequence timing of the project through 2D storyboard drawings.
- Design: The final look of the project is decided at this stage; including the concept design, character design, costumes, prop design, and environment. The mood and the concept of designs must be fully conveyed here. If you want to know the ins and outs of character design, check out the article about shape language in character design.
- Production: The production stage is where all previous efforts must pay off and transform into action. At this stage, visual elements of the 3D animation will be handed out to the designated teams and artists. Team leaders make sure time frames, and quality matches those of the determined plan in the pre-production stage and goes as smoothly as possible. The outcome of this stage shapes the entirety of the 3D animation.
- 3D Layout: Simply put, a 3D version of the 2D animatic is called a 3D layout. The 3D layout contains basic 3D attributes such as the characters’ size, shape, environment, a simple animation of the characters, proxy geometry, et cetera.
- 3D Modeling: 3D modeling is the process of developing a geometric surface representation of any object in a specialized 3D software such as Maya or 3Ds Max.
- 3D Texturing: The process of creating and applying textures (colors and surface properties) to a 3D model is called 3D texturing. Before coming to the texture artist, 3D models are usually in a default shaded flat color.
- 3D Rigging: During the rigging process, a bone structure is put into the 3D object so that the animators can move different parts of the geometric object (in character rigging, for example) as quickly and efficiently as possible.
- 3D Animation: The movements of the 3D objects or characters in a scene or setting are created during the animation stage. Animation is usually the most crucial and time-consuming part of producing a 3D animated video.
- A 3D animator animates almost everything, but elements like hair, fur, water, fire, clothes, or dust; key-framing them would be too difficult or even impossible.
- Lighting: Just like real-world lighting in photography or filming, 3D animation lighting is the stage at which the mood of a 3D scene or sequence is created through light based on the pre-production designs.
- Rendering: When dealing with a 3D animation, every scene is separated and rendered into multiple layers, including objects, colors, background, foreground, shadows, highlights, et cetera. The layers are going to be united again in the post-production stage (Compositing).
- Post-production: At this stage, the final touches are added to the project to make it look polished and professional (the definition of polished and professional might differ in various projects, of course). Post-production artists have a number of tools that can make up the look of a project in whatever way they want.
- Compositing: To make a final output, the layers rendered previously are put together again in compositing. The layering process can be as simple as putting 2 layers together or as complex as matching hundreds of layers and adjusting their properties.
- 2D VFX: Some visual effects, such as sparks, dust, raindrops, camera shakes, et cetera, are more easily achieved in a 2D environment at the end of the project without sacrificing the quality. These effects are usually mixed with other layers in compositing.
- Color correction: Also known as color timing or color grading, color correction is literally the last adjustment we make to a 3D animation in the pipeline. This step makes each shot and the whole project look more consistent.
- Final output: There are different options out there regarding the output format of the pipeline. However, the most common type is a digital video which is compatible with most digital devices and can be played on the internet.
- 3D animation production pipeline has three main stages: Pre-production Production Post-production.
- Student works
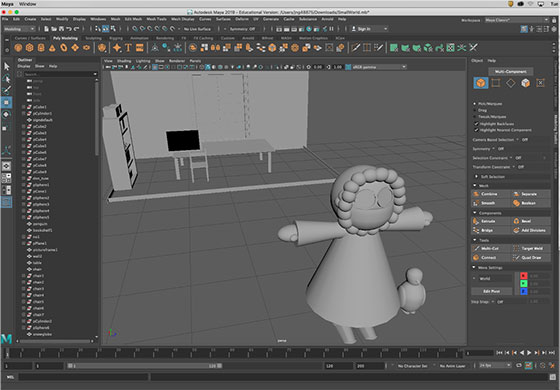
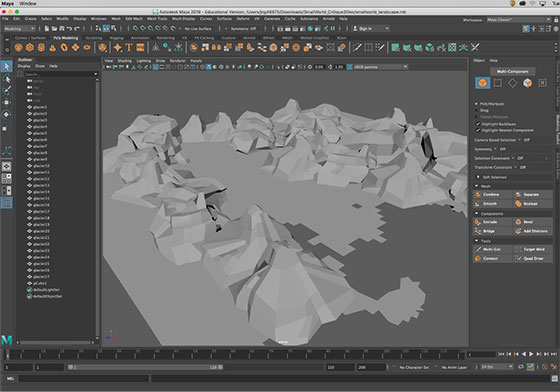
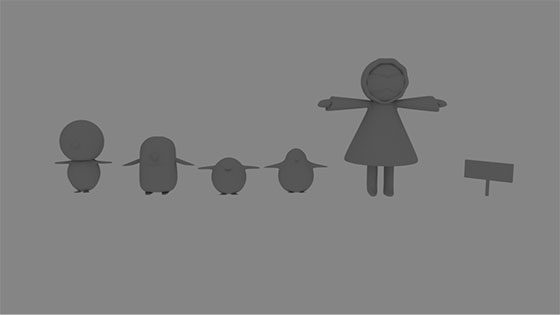
- Small World by Savannah Mohr


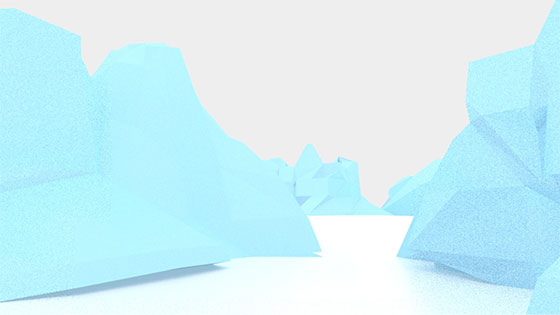



- And I Dreamt I Was Alive by Travis Harrell





- Small World by Savannah Mohr
- What is an animation pipeline?
- Srudent animations

- Animation at WKU

- Begun in Spring 2018, the Computer Animation program is one of the fastest growing programs at WKU.
- The Computer Animation program assists to prepare students for careers in the creative technological fields such as computer animation, motion graphics, film, television, videography, and multi-media design; for further graduate study; and for developing an individual contemporary art practice.
- Ever since the program was launched a few years back, graduates of our program have gone to work for several animation and design firms. Along with creative representation at galleries, few have won awards for their animated films from short animation festivals, and many have shown their works in academic settings around the world.
- The alumni and faculty have consistently pushed the edge publicly as to what it means to be a computer artist and continue to maintain that intensity today.
- Whether you are an aspiring animator or not, learning computer animation will greatly expand your creative horizon.
- Computer Animation propgram at WKU is the only program its kind in Kentucky.
- Minor: requires 21 semester hours. At least 1/2 of the hours required for the minor must be earned in courses numbered 300 and above. 1/3 of the hours in the minor must be earned at WKU.
- Introductory (choose one) 3 Hours
ART 130 2-D Design
ART 131 3-D Design
ART 140 Drawing
- Required (choose four) 12 Hours
ANIM 210 Introduction to Computer Animation
ANIM 220 3D Modeling I: Environment
ANIM 310 Computer Animation I
ANIM 344 Computer Animation II
- Restricted Electives (choose two) 6 Hours
ANIM 320 3D Modeling 2: Character Design and Development
ANIM 330 Sound and Image
ANIM 444 Computer Animation III
ART 497 Special Topics in Animation
BCOM 378 Film Animation
The Minor takes *at least* three semesters to complete. Prerequisite courses are listed [in parentheses].
- Semester 1
Foundations course:
ART 140 Drawing or ART 130 2D Design or ART 131 3D Design
ANIM 210 Introduction to Computer Animation
ANIM 220 3D Modeling I: Environment
- Semester 2
ANIM 310 Computer Animation I [ANIM 210 or ANIM 220]
Restricted Elective 1 [prerequisites vary]
- Semester 3
ANIM 344 Computer Animation II [ANIM 310]
Restricted Elective 2 [prerequisites vary]
- Introductory (choose one) 3 Hours
- Minor: requires 21 semester hours. At least 1/2 of the hours required for the minor must be earned in courses numbered 300 and above. 1/3 of the hours in the minor must be earned at WKU.
- Major: requires 79 semester hours. At least 1/2 of the hours required for the minor must be earned in courses numbered 300 and above. 1/3 of the hours in the minor must be earned at WKU.
- Foundations (15 Hours)
- ART 130 2-D Design
- ART 131 3-D Design
- ART 140 Drawing
- ART 105: Art History Survey 1
- ART 106: Art History Survey 2
- Basic Studio (9 Hours)
- Basic Studio 1
- Basic Studio 2
- ART 243 Digital Media
- Required drawing/illustration (6 hours)
- ART 240 Drawing
- ART 340 Drawing / ART 431 Illustration
- Upper-level elective studio (6 hours)
- UL studio 1
- UL studio 2
- Upper-Level Art History Requirements (6 hours)
- UL Art History 1
- UL Art History 2
- Final Semester
- ART 434 Capstone Seminar (1 hour)
- ART 434 Capstone Seminar (1 hour)
- Basic Animation (12 hours)
- FILM 100 Film Industry and Aesthetics
- FILM 202 Basic Film Production
- ANIM 210 Introduction to Computer Animation
- ANIM 220 3D Modeling I: Environment
- Advanced Animation Requirements (18 hours)
- ANIM 310 Computer Animation I
- ANIM 320 3D Modeling 2: Character Design and Development
- ANIM 330 Sound and Image
- ANIM 344 Computer Animation II
- ANIM 444 Computer Animation III
- ART 497 Special Topics in Animation
- Animation Restricted Electives (6 hours)
- ART 340 Drawing
- ART 341 Drawing
- ART 431 Illustration
- ART 436 Electronic Illustration
- ART 497 Special Topics in Animation
- UX 330 Interactive Design
- BCOM 378 Film Animation
- CS 301 Game Programming
- FILM 355 Film Sound
- Foundations (15 Hours)
- Our animation facilities
Among our four Mac and one PC computer labs in the Department of Art & Design, rooms FAC 438 (Mac) and 254 (PC) are the hubs of computer animation. Our labs each have 18 workstations, and the current Adobe Creative Cloud, Autodesk Maya, 3DS Max, and other relevant software is accessible day and night.
- Begun in Spring 2018, the Computer Animation program is one of the fastest growing programs at WKU.




