
ANTH 336 New World Prehistory
Dr. Darlene Applegate
Fall 2006
Mesoamerica Culture
Area
Aztec Civilization
TIME PERIOD
Post-Classic Period
AD 1200-1521
LOCATION
central highlands
Valley of Mexico, Lake Texcoco area
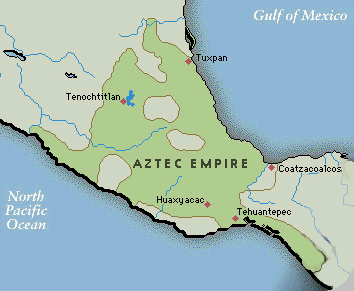
Map Showing Extent of Aztec Empire, Location of Aztec
Capital at Tenochitlan on Lake Texcoco, and Locations
of Other Aztec Sites.
http://www.ucalgary.ca/applied_history/tutor/eurvoya/aztec.html
ORIGINS
according to traditional history, originated from Toltec
prior to development of complex society, Aztec were vassels of many
other cultures
settled on island in Lake Texcoco and established civilization
SUBSISTENCE
agriculture based on chinampas
agricultural fields constructed on the
edges of lakes
each plot was constructed of a "cage" of vertically driven wooden posts
and infilled with sediment
plots were accessed by watercraft

Artist Reconstruction of Chinampas Construction and Use.
http://intranet.whitefriars.vic.edu.au/public/faculties/sose/students/James%20M/History%20Assignment/aztec_beginnings.htm
DIAGNOSTIC ARTIFACTS
chinampas agriculture
see above
large-scale landscape engineering projects
included dikes, roads,
aquaducts, causeways
pochteca
a special socio-economic class of
merchants or traders
above farmer class, below noble and military classes
often occupied special sections of Aztec cities
membership in pochteca class was hereditary
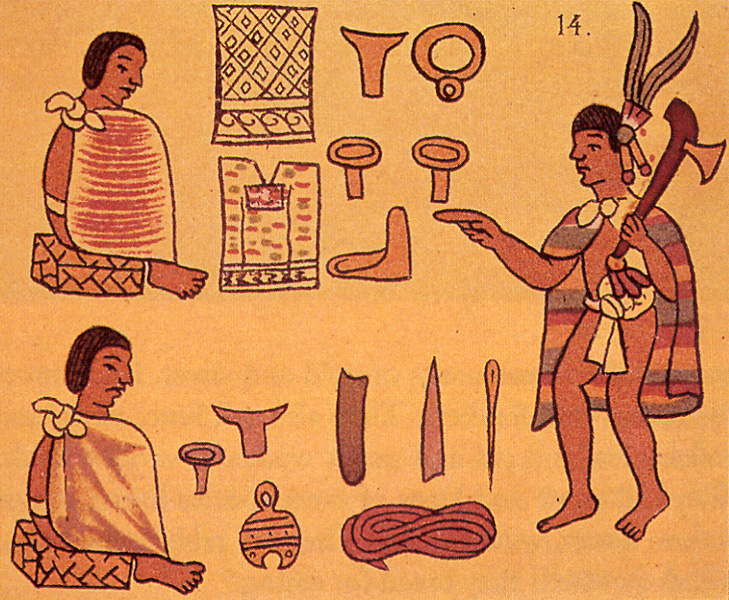
Portion of the Florentine Codex Showing Two
Pochteca Displaying Goods
for Trade, Including Textiles and Personal Ornaments of Gold and
Obsidian.
http://www.latinamericanstudies.org/aztec-trade.htm
experts in metallurgy
metal working activities involved
smelting (melting metal ores) and alloying (combining metal ores)
used gold, silver, copper
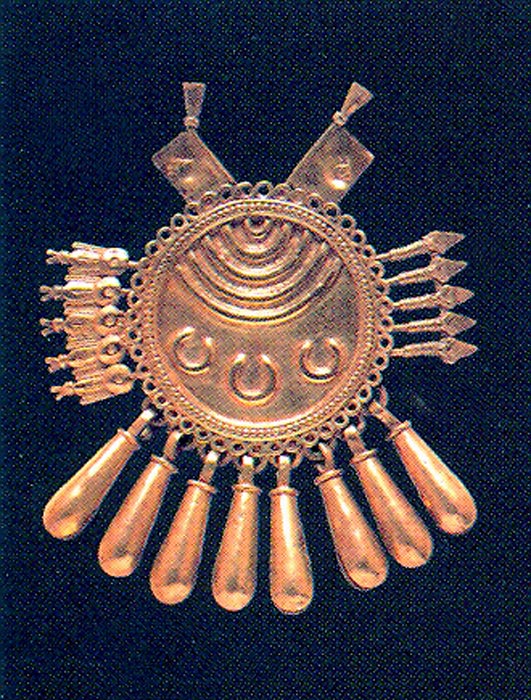


(Left) Image of Aztec Metalsmiths from Florentine Codex and (Right)
Gold Aztec Pendant of Shield and Arrows.
http://www.mexicolore.co.uk/index.php?one=azt&two=ask&tab=ans&id=16
SETTLEMENT STRATEGY
settlements were often fortified for defensive purposes
cermonial centers laid out on grid system
hierarchy of site sizes, with cities/ceremonical centers at the highest
level
SITES
Tenochitlan (capital)
- built on an island in Lake Texcoco
- established in AD 1325
- covered an estimated 13.5 sq km, divided into four major districts
- accessed from the lake shore by three artificial causeways to the
north, west, and south
- monumental public architecture in the walled ceremonial center of
the city included major temple pyramids (Templo Mayor, Templo
Quetzalcoatl, Templo Huitzliopochtli), minor temples, 100-room royal
palace with zoo, ball court, skull rack, platforms, and market place
- population reached an estimated 200,000 at its peak
- sacked by Spanish conquistadors in AD 1519-1521
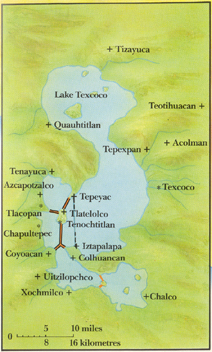

(Left) Location of Tenochitlan on an Island in Lake Texcoco, central
Mexico.
http://intranet.whitefriars.vic.edu.au/public/faculties/sose/students/James%20M/History%20Assignment/aztec_beginnings.htm
(Right) Artist Reconstruction of the Western Causeway Providing
Access to the Island Capital of Tenochitlan.
http://home.freeuk.net/elloughton13/aztec.htm
POLITICAL ORGANIZATION
elements of a theocracy: hereditary line of semi-divine kings,
including last ruler Moctezuma
created an empire through militaristic expansion
DECLINE
conquered by Spanish (Hernan Cortes) over a three-year period (AD
1519-1522)
contributing factors weakened the Aztec: drought, internal strife
and
civil conflict, strains on empire by extracting tribute from subjugated
peoples, disease (at least 80% died after European contact)
Return to New
World Prehistory Home Page
Visit the Western Kentucky University
Home
Page, Western Online
Page composed by Darlene Applegate, darlene.applegate@wku.edu
Last updated on November 7, 2006
All contents copyright (c), 2006. Western Kentucky
University.








