
ANTH 336 New World Prehistory
Dr. Darlene Applegate
Fall 2006
Arctic/Subarctic
Culture Area
Environmental Characteristics
BOUNDARIES
- east = Pacific Ocean, Bering Sea
- west = Atlantic Ocean
- north = Arctic Ocean
- south = Woodlands, Great Plains, Far West (Plateaus, Northwest
Coast) culture areas
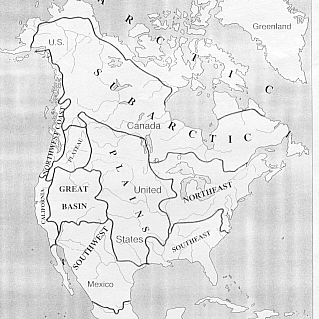
Boundaries of Arctic/Subarctic Culture Area.
OVERVIEW OF ARCTIC
- northernmost of the two zones
- includes western Alaska, northern Canada, around Hudson Bay,
northern coast of Quebec and Labrador, coast of Greenland
- thousands of miles of coastline dotted by hundreds of islands
- tundra biotic zone with no trees and few plants
- long winter of 8-9 months
- arid with < 10" per year of precipitation
- lakes and streams present
- permafrost conditions
- predominant terrestrial mammal is caribou
- predominant aquatic mammals are whale, seal, and walrus

Tundra Environment.
OVERVIEW OF SUBARCTIC
- southernmost of the two zones
- subdivisions are Alaska, Yukon Territory, Northwest Territory,
British Columbia, Barren Land
- thousands of square miles of land
- mountain ranges include Brooks, some with volcanoes
- mountain glaciers present
- boreal or alpine biotic zone with scattered short trees like
spruce, birch, poplar, balsam, willow shrubs, grasses, lichens
- permafrost conditions
- lakes, streams, swamps, and marshes present
- winter season lasts six months and is more severe due to greater
precipitation
- predominant terrestrial mammal is moose

Contemporary Boreal Wetlands in Canada.
POSITIVE ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
1. year-round animal resources
- marine resources: seal, walrus, sea otter, sea lion, whale,
fish, shellfish
- land mammals: caribou, bear, moose, elk, rabbit, musk
ox
- aquatic resources: salmon, fish, shellfish
- used for subsistence, tool manufacture, house construction,
clothing
Aquatic Animals: Beluga Whale, Seal,
Walrus.
Terrestrial Animals: Caribou, Moose,
Musk Ox.
ENVIRONMENTAL CHALLENGES
1. limited plant resources
- seasonally available
- not used much for subsistence
- used to limited extent for tool manufacture, house construction
2. permafrost (part of the soil remains frozen year-round, while
upper levels thaw during the warm season)
- inhibits movement during warmer seasons

Permafrost (White Layer) Underlying Unfrozen Soil (Dark Layer).
3. severe weather and climate
- long winter, low light, snow storms,
frigid temperatures
- limits human activity and movement
Return to New
World Prehistory Home Page
Visit the Western Kentucky University
Home
Page, Western Online
Page composed by Darlene Applegate, darlene.applegate@wku.edu
Last updated on September 26, 2006
All contents copyright (c), 2006. Western Kentucky
University.









