

Note: The portion of the Mediterranean-Aegean area
that
is considered by some to be a food production hearth is southeast
Europe,
including Greece, Crete and Aegean islands, and the Balkans. Food
production spread through the Mediterranean and through rest of Europe
from here.
GENERAL TRENDS
1. food production was an indigenous development (in some places) coupled with some influence from the Near East
2. animals and plants were domesticated at about the same time
3. possible indigenous development of plow, or it spread from the Near East
4. there were three phases of development in shift from food collection to food production:
ANIMAL DOMESTICATES
most important were cattle, sheep, goats, pig; also dog
earliest evidence of domesticated cattle, sheep and pigs is about 7000 B.C. from Argissa-Maghula in Greece
earliest evidence of domesticated goats is about 6000 BC from
Franchti
Cave in Greece


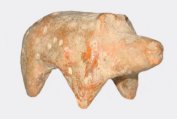
Domesticated cattle, domesticated
pig, and clay effigy of pig from Greece.
PLANT DOMESTICATES
most important were wheat and barley, olive, grape
also fig (fruit), flax and millet (cereal grains), lentils and fava beans (legumes)
earliest evidence of domesticated wheat and barley is about 7000 B.C. from Argissa-Maghula in Greece
earliest evidence of domesticated lentils is 7000 BC at Franchti Cave and 6000-5800 BC from Grotta dell’Uzzo in Sicily
earliest evidence of domesticated millet is about 3500 BC
olive and grape were used to make oil and wine, respectively, which
were stored in pottery vessels called amphorae (singular is amphora);
amphorae had two handles and often had tapering bases, which required
storage by hanging or using a stand
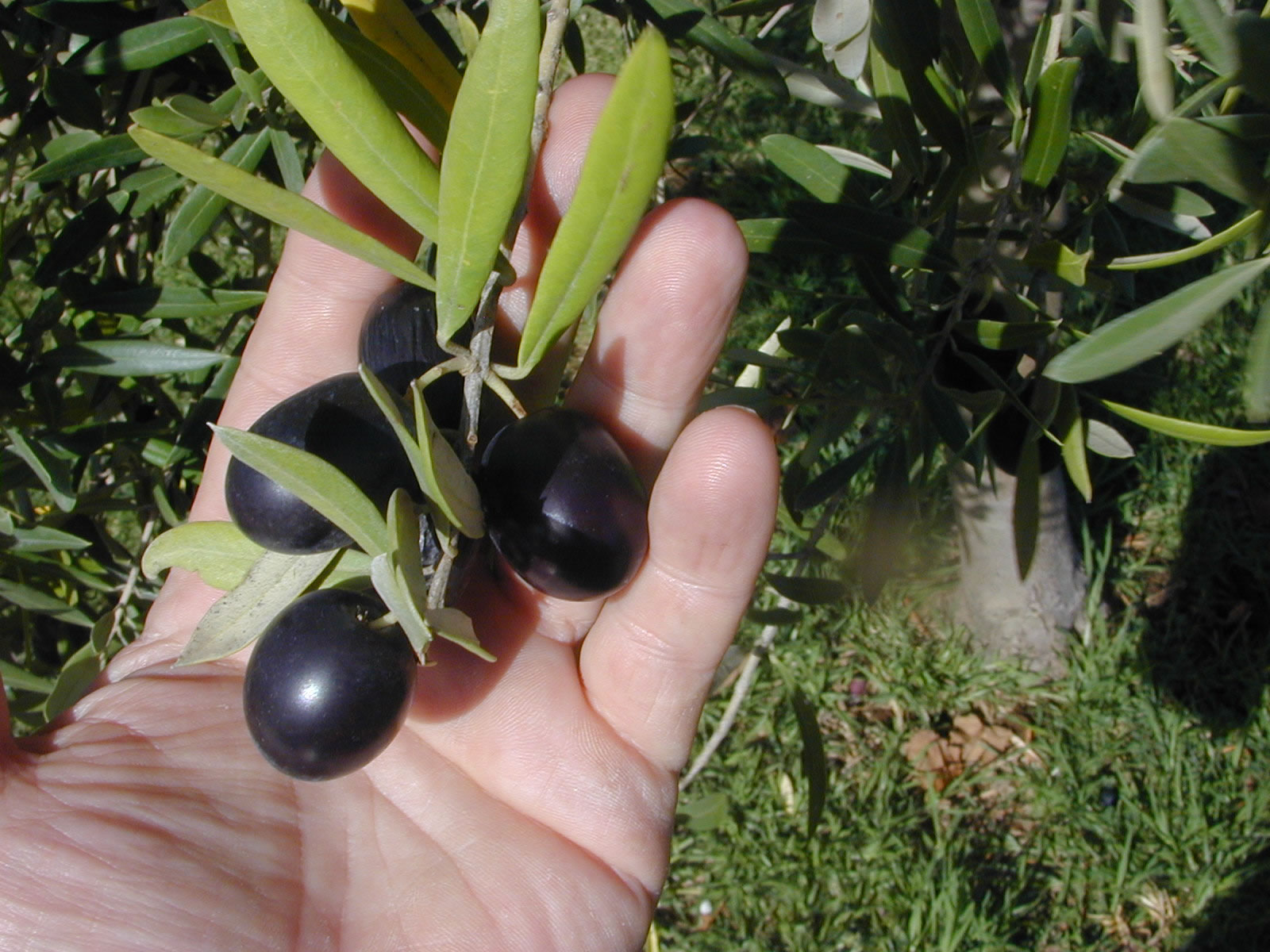



Olives, grapes, and mphora in stand.
FOOD PRODUCTION
may be as early as 6000 BC
if this early date is correct, may be quickest rate of change in Old World from food collection to food production (from the time the first domesticates are evidenced to the time people became reliant on domesticates)
spreads from southeast Europe into rest of Europe:
clear evidence that farming and herding are well established in Greece by 6000-5500 BCplow agriculture began about 3600 BC and was well established by about 2600 BCMediterranean coast by 5000 BC
central and eastern Europe by 5300-4000 BC
to northwest Europe by 3500 BC
Diffusion of food production from Aegean
into rest of Europe.
some archaeologists have suggested that wheat use spreads from
southeast
Europe into Indus Valley
REFERENCES
Price and Feinman (2001), Feder (2000), Fagan (2002), Dennell (1983)