

DATING METHODS
most chronological units are based on changes in pottery stylistic
types
other types of material culture used to delineate time periods are
artwork, tools, and architecture
absolute dates derive primarily from radiocarbon dating
CHRONOLOGICAL UNITS AND CULTURE HISTORY IN MESOPOTAMIA
Mesopotamia is the area of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in present-day Iraq
Eridu Period (6000-5300 BC)
small villages, most on upper drainages of Tigris and Euphrates
beginning of irrigation
culture systems: Hassuna, Samarra, Halafian
chiefdom level of organization
'Ubaid Period (5300-3600 BC)
divided into four subdivisions
'Ubaid 1 saw initial colonization of southern Mesopotamia delta area
by irrigation farmers
by 'Ubaid 3 and 4, culture of entire Mesopotamia essentially uniform
priests control economy
lots of clay artifacts cuz stone scarce, cast copper tools
culture systems: 'Ubaid, which began in lower Mesopotamia
core area southern Mesopotamia, reversing earlier trend of biggest
advances in north Mesopotamia
early temple sites like Eridu and Tell Al 'Ubaid in southern
Mesopotamia,
temples were precursors to ziggurat
also sites in northern Mesopotamia, like Tepe Gawra
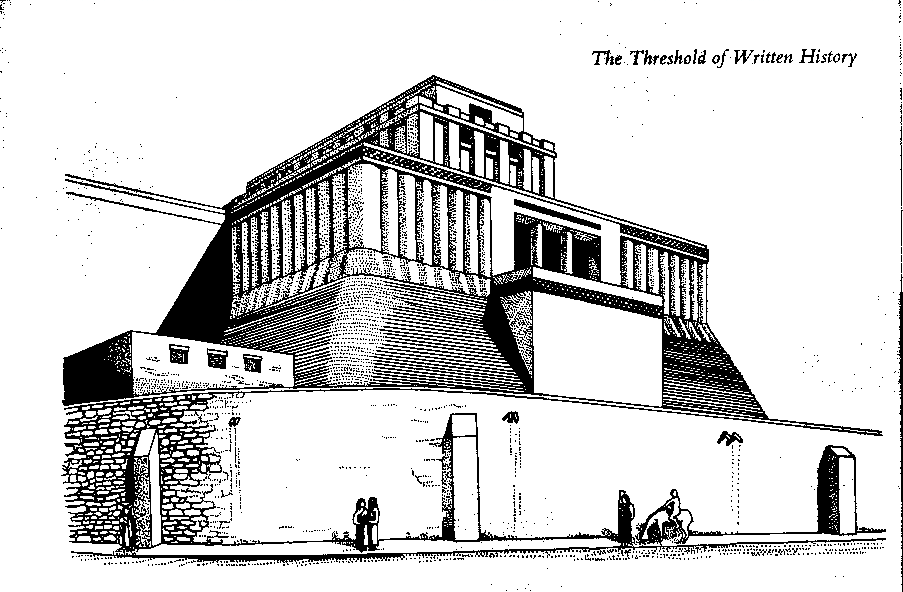
The temple at Eridu, Iraq.
Uruk or Warka Period (3600-3100 BC)
southern Mesopotamia gains primacy in development of urban life, but
distributed through Mesopotamia and beyond, with increasing complexity
in Zagros foothills
diagnostic artifacts related to changes in pottery, especially
development
of wheel made
glyptography (seal use) begins
first city in Near East is Warka (ancient Uruk), type site,
population
estimated at 10,000+ at this time (not its peak), ziggurats
increase in number of temple towns and villages
social hierarchy beginning, elite priest class with control based
at temples/ziggurats
divided into early and late
Early Uruk (3600-3400 BC) temple platform construction continues,
21 sites known
Late Uruk (3400-3100) mass production of pottery, earliest writing at Ur about 3400 BC, standardization of measures, earliest monumental architecture at Warka/Ur site is Anu ziggurat (sky god), 123 sites known -- some trappings of complex society

Ziggurat for Anu at Ur, Iraq.
Jemdet Nasr Period (3100-2900 BC)
not well known archaeologically
previous trends continue, and urban organization stabilized and
solidified
architectural and organizational centers of cities were temples
about 10 major centers in southern Mesopotamia, including Warka
major centers in middle Mesopotamia are Khafaje and Tell 'Uqair; in
north, Brak
copper use widespread and increase in trade activity
development of Zagros cultures: Proto-Elamite
Proto-Literate or Early Dynastic Period (2900-2400 BC)
writing is widespread, not just economic uses
little change in utilitarian artifact suite
plano-convex brick construction introduced
first copper objects (figurines) made with lost-wax technique
first city fortifications, especially massive mud-brick walls
development of secular power; constant power struggles within and
between cities
independent city-states developed from temple cities; Warka at peak
population of 50,000 and Ur is city-state, both by mid Early Dynastic;
city is basic political unit; other city-states are Nippur, Kish, Mari,
Eridu; each had patron deity
growth of urban centers accompanied by rural depopulation (fewer
sites,
many larger in size, hierarchy)
social stratification clearly developed; first evidence of slaves;
craft specialization
trade much increased
first city-state (Sumeria) and beginnings of nation and empire (Elamite) in Near East

Sumerian clay tablet with cuneiform
writing.
Akaddian, Gutian and Ur III periods round out third
millennium and bring us fully into the historic period
CHRONOLOGICAL UNITS IN THE LEVANT
the Levant is the strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea that marks the intersection of Africa and Asia; Israel and Lebanon are two current countries in the Levant
Yarmukian Period (5300-4100 BC)
Beersheba-Ghasullian Period (4100-2900 BC)
Early Bronze Age Period (post 2900 BC)
CHRONOLOGICAL UNITS IN KHUZISTAN
Khuzistan lies east of the Tigris-Euphrates Rivers in Iran's alluvial and piedmont zones
Susiana Period (5300-4000 BC)
increase in population
about 40 sites, including Tepe Sabz and Susa, Iran
irrigation in some areas was necessary
Susa A Period (4000-3600 BC)
peak in population growth, which was earlier than in Mesopotamia but
was not sustained
settlement size hierarchy, with sites like Susa at top level
Susa B Period (3600-3400 BC)
Susa C Period (3400-3100 BC)
Susa D Period (post 3100 BC)

Location of Susa, Iran.

Choghazanbil ziggurat at Susa, Iraq.
REFERENCE
Redman, Charles L.
1978 The Rise of Civilization. W.H. Freeman, San
Fransisco.
To view
sources of images reproduced in this web page, left click on the image
and select Properties.
The URL is
listed under Alternate Text.