

 MATERIAL CULTURE refers to the tools
and other fabricated items used by humans to interact with the
natural/cultural environment
MATERIAL CULTURE refers to the tools
and other fabricated items used by humans to interact with the
natural/cultural environment LITHIC is a tool or other item
made of stone
LITHIC is a tool or other item
made of stone POTTERY is a tool or other item made
of sun-dried or fired clay
POTTERY is a tool or other item made
of sun-dried or fired clay FOOD COLLECTING is the reliance on
wild plants and/or animals for the
majority of the group's subsistence;
FOOD COLLECTING is the reliance on
wild plants and/or animals for the
majority of the group's subsistence;
also called hunting-gathering
or hunting-gathering-fishing
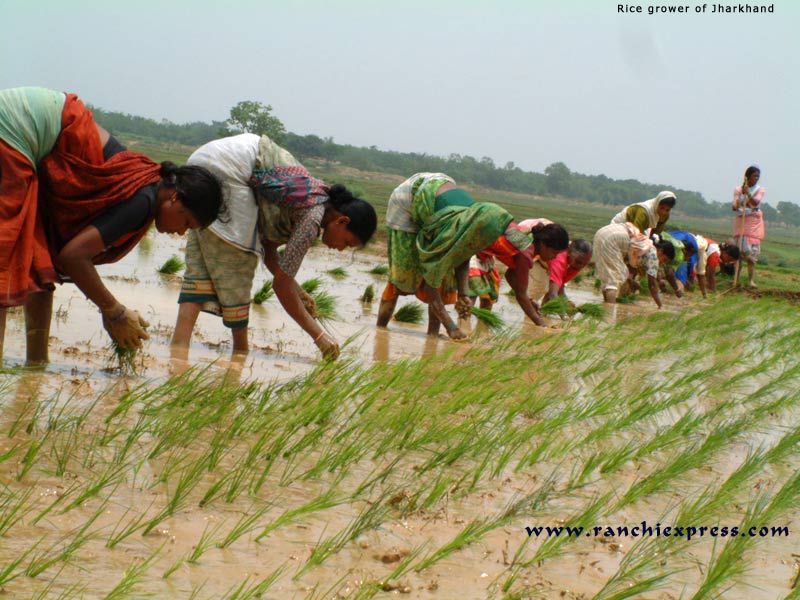 FOOD PRODUCTION is the reliance on
domesticated plants and/or animals
for the majority of the group's subsistence;
FOOD PRODUCTION is the reliance on
domesticated plants and/or animals
for the majority of the group's subsistence;
includes agriculture, farming,
horticulture, gardening, stockbreeding, herding, pastoralism
 WILD plants and animals are those
that exist in nature without human
intervention and exist in a natural home range
WILD plants and animals are those
that exist in nature without human
intervention and exist in a natural home range
 DOMESTICATES are plants and animals
whose form is the result of human
intervention in the breeding process,
DOMESTICATES are plants and animals
whose form is the result of human
intervention in the breeding process,
plants and animals that cannot survive
without human intervention, and/or plants and animals that live outside
their
natural home ranges; plant domesticates called "cultigens"
 DOMESTICATION is the selective
breeding process by which a wild plant or animal
becomes a domesticate
DOMESTICATION is the selective
breeding process by which a wild plant or animal
becomes a domesticate
SETTLEMENT
 MOBILITY is
residential movement on a continual basis without
significant
settlement permanence
MOBILITY is
residential movement on a continual basis without
significant
settlement permanence
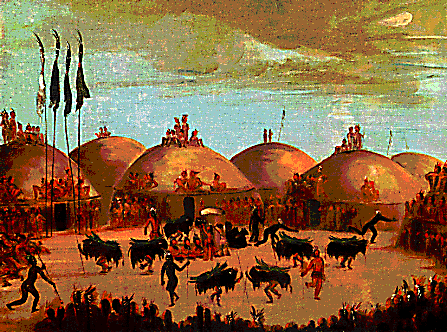 SEDENTISM is
year-round, permanent residence in one location
SEDENTISM is
year-round, permanent residence in one location
VILLAGES are early
sedentary settlements with low population
densities
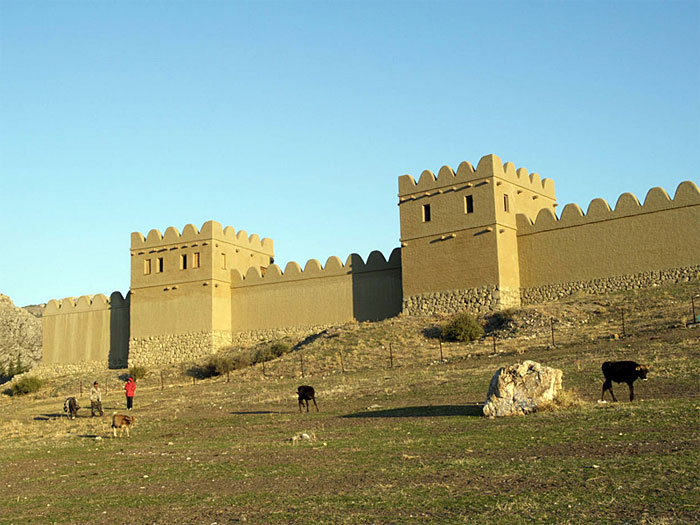 CITY or URBANISM is a
relatively high density of people living
within
a limited space on a permanent basis; characteristics are (1)
nucleation (living close together in a limited area), (2) high
population density (at least 100 people per square kilometer), (3)
non-farming sector of society, (4) craft or occupational
specialization, (5) social stratification or social ranking, and (6)
surrounding subsistence area to support urban center
CITY or URBANISM is a
relatively high density of people living
within
a limited space on a permanent basis; characteristics are (1)
nucleation (living close together in a limited area), (2) high
population density (at least 100 people per square kilometer), (3)
non-farming sector of society, (4) craft or occupational
specialization, (5) social stratification or social ranking, and (6)
surrounding subsistence area to support urban center
SOCIAL
ORGANIZATION
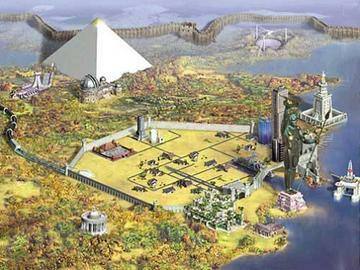 COMPLEX SOCIETIES or STATES
or CIVILIZATIONS have some combination
of
the following characteristics
COMPLEX SOCIETIES or STATES
or CIVILIZATIONS have some combination
of
the following characteristics
(based on V. Gordon Childe and Elman Service)
1. agricultural basis (subsistence economy is based on food production and a surplus economy)2. urbanized (based on cities, majority of population lives in cities)
3. complex social organization (permanent, hierarchically arranged social class system based on economics, religion or ethnic background)
4. full-time occupational specialization or craft specialization (food producers versus nonproducers; nonproducers include leaders, priests, merchants, members of the armed forces, craftspeople and artisans)
5. territorial basis (communities within the area have some form of allegiance, borders are defended)6. concentration of surpluses by the state (usually food but also other materials; related to state control of exchange and trade, redistribution and taxation)
7. strong, centralized government with a professional ruling class (inclusion in ruling class is often, but not always, separate from kinship)
8. force as a means of social control (military, police, judicial system)
9. true law (a codified set of rules of behavior)
10. monumental public works of architecture (pyramids, temples, irrigation systems, roads)
11. standardized artworks (flags, clothing, artistic icons, and related artwork that symbolize the state or social classes within the state)
12. writing systems (hieroglyphic, alphabetic, iconographic)
13. advances in math, geometry and astronomy (to lay out cities, to build monumental works, to keep records of taxes or trade, and to follow agricultural cycles)
14. large population size (greater than 20,000)
 there are FOUR TYPES OF COMPLEX
SOCIETIES: theocratic states, city states, nation states, and
empires
there are FOUR TYPES OF COMPLEX
SOCIETIES: theocratic states, city states, nation states, and
empiresNATION STATE is a centralized economic and political power organized along political and territorial lines, with hierarchical and differential access to resources, and with monopoly on power; more unified than city states; has a city that serves as capital
EMPIRE
is a
centralized economic and political power that crosses
political
and territorial lines; groups are subjugated politically, militarily,
economically,
socially, religiously; tribute/ taxation
 KINGDOMS may be
considered complex or semi-complex societies but they
differ from states in that leadership is not coercive,
KINGDOMS may be
considered complex or semi-complex societies but they
differ from states in that leadership is not coercive,
leadership tends
to be based on kinship, urbanism is lacking, and monumental public
works
are usually absent or less elaborate
TIME
UNITS IN ARCHAEOLOGY
1550
B.C. NUMERICAL TIME UNITS are expressed in
number format
Shang
Dynasty PERIOD TIME UNITS
are
expressed in non-numerical format but in relative order from oldest to
youngest
CULTURE
AREAS
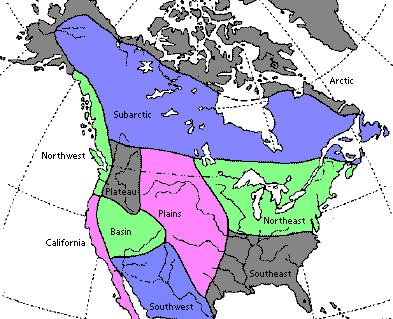 CULTURE AREA is a
geographic region in which the people shared in common a set of
cultural traits and behaviors
CULTURE AREA is a
geographic region in which the people shared in common a set of
cultural traits and behaviors
originally defined by cultural anthropologists but adopted by
archaeologists, with some minor changes
Old World culture areas covered in this class are those (with
one exception) where complex societies were an indigenous development:
Near East, Mediterranean-Aegean, lower Nile, tropical Africa, temperate
Europe, Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and China
To view the
sources for the images
included on this web page, point to an image and left-click to select
Properties.
The URL for the source of the image is listed under Alternate Text.