ANTH 336 New World Prehistory
Dr. Darlene Applegate
Fall 2006
Mesoamerica Culture
Area
Lowland Maya Civilization
TIME PERIODS
Pre-Classic Period
1000 BC to AD 250
Classic Period
AD 250 to AD 900
Post-Classic Period
post-AD 900
LOCATION
lowland rain forests of the Yucatan Peninsula and “Peten” areas of
Mesoamerica, in present-day countries of Guatemala, Belize, Mexico
also in highlands of western Honduras and El Salvador
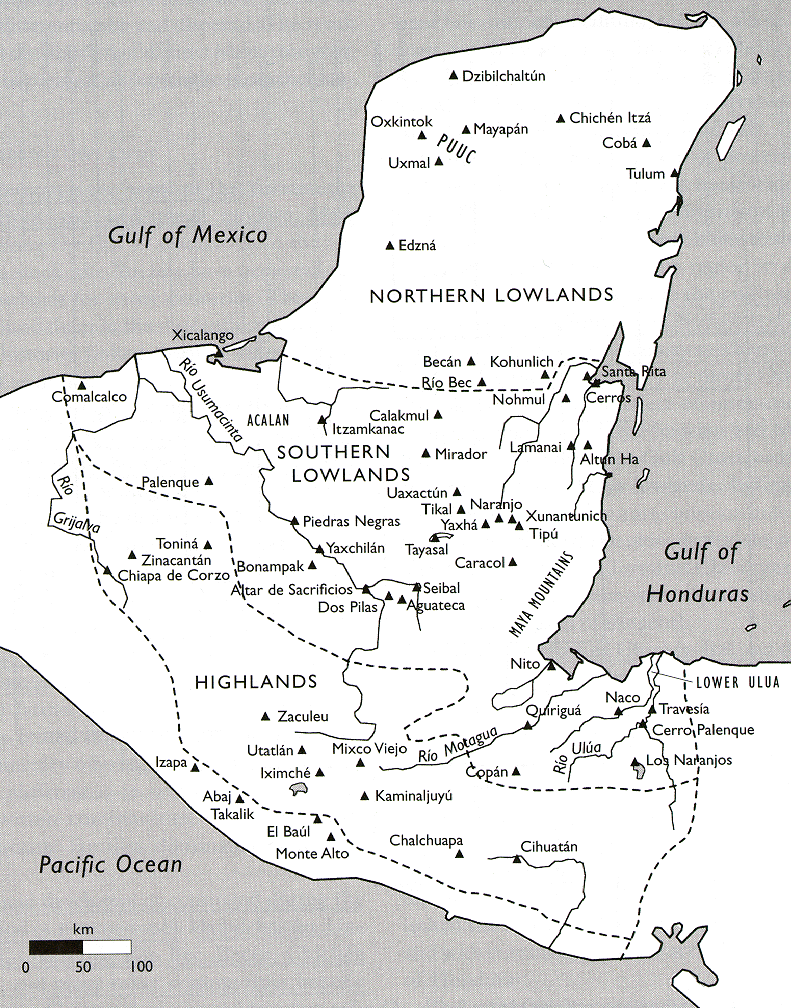
Map Showing the Lowland and Highland Zones of the Maya Territory,
Including Important Maya Sites.
http://www.latinamericanstudies.org/mayas.htm
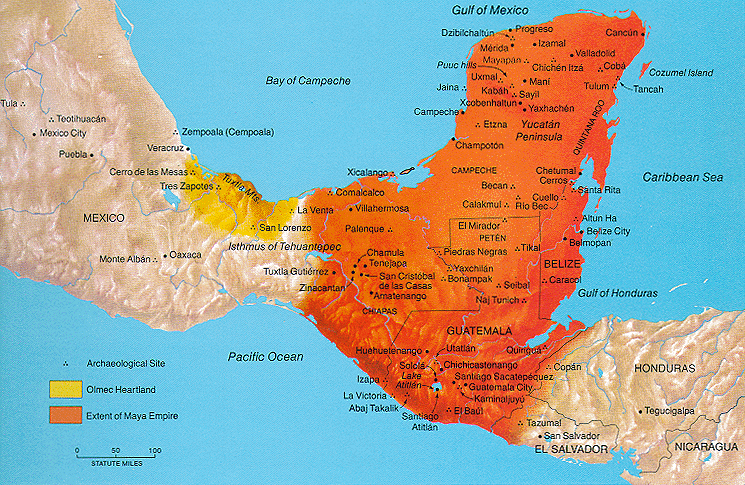
Map Showing the Extent of the Maya Civilization, Including Important
Maya Sites.
http://www.latinamericanstudies.org/mayas.htm
ORIGINS
earliest developments occurred in the highlands to the south
Maya civilization was an indigenous development related to trade,
political alliances, economic shortages, overcoming
environmental challenges, the develoment of silviculture (forest
management practices), or some
combination of these factors
SUBSISTENCE
agriculture based on raised fields

Aerial Photograph of Relict Raised Fields in Quintana Roo Province
of Mexico.
http://www.agroecology.org/cases/prehispanic.htm
DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
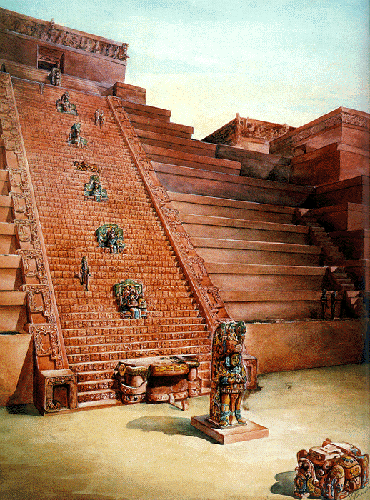
roof combs on pyramid temples
a roof comb is a stone construction,
often with open lattice work, atop pyramid temples
roof combs gave the appearance of greater height of pyramid temples
roof combs often were carved or painted with zoomorphic or
anthropomorphic motifs as well as texts



(Left) Roof Comb on the Temple of the Inscriptions at the Maya Site of
Palenque, Mexico.
(Center) Artist Reconstruction of Vulture Motif on Roof Comb.
(Right) Open Lattice Roof Comb on Temple at Yaxchilan, Mexico.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maya_civilization
http://www.civilization.ca/civil/maya/mmp02eng.html
http://www.questconnect.org/mexico_yaxchilan_photos.htm
corbeled vaults
corbeled vaults are arches formed by
laying consecutive courses of horizontal stone with progressively
smaller gaps to create a curved or triangular opening


(Left) Schematic of Corbeled Vault Construction and (Right) Corbeled
Vault at the
Governor's Palace at the Maya Site of Uxmal, Mexico.
http://www.answers.com/topic/corbel-arch
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Image:Arco_maya.jpg
SETTLEMENT STRATEGY
settlement system: primary ceremonial complexes with surrounding
domestic dwellings as secondary complexes
SITES
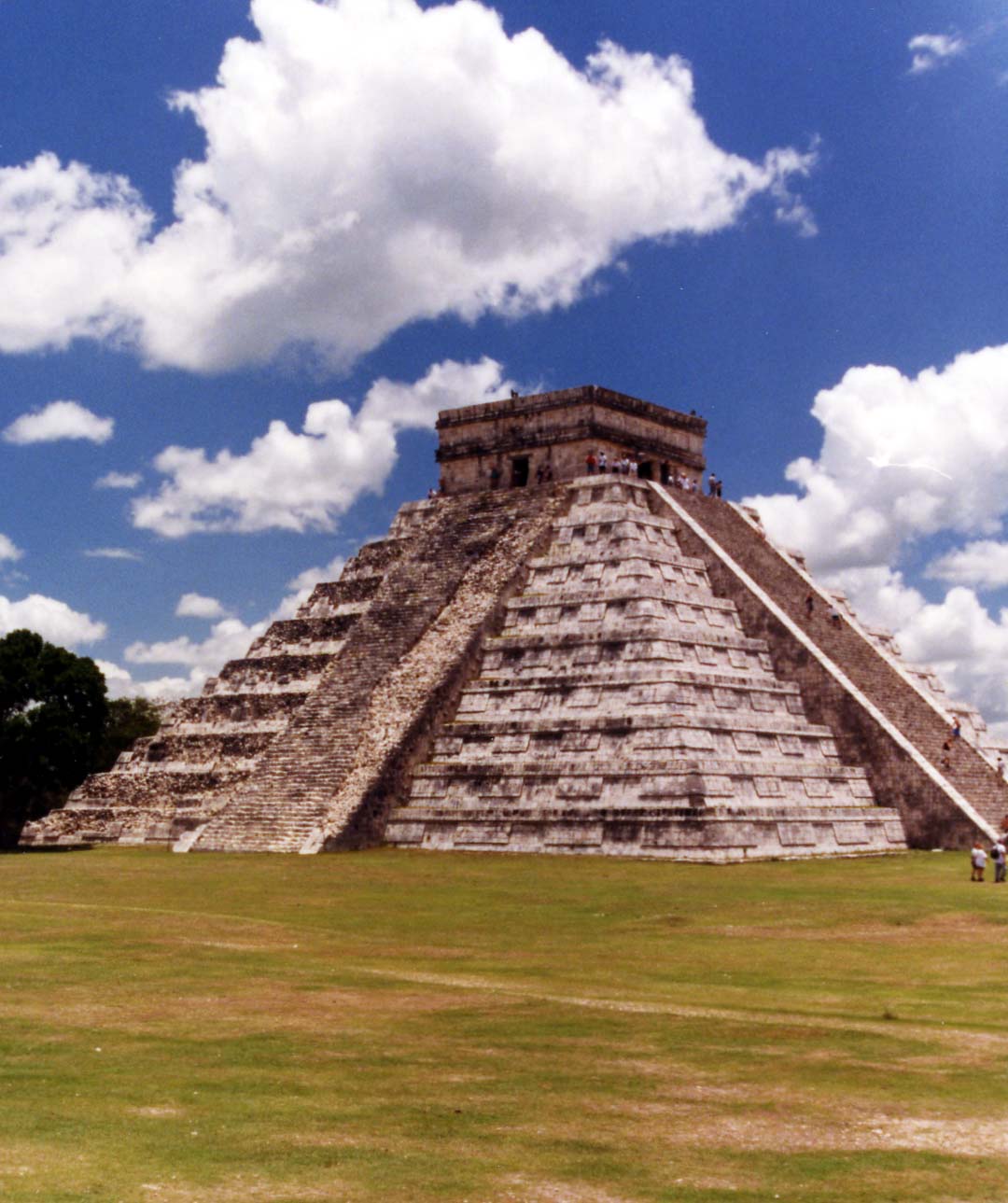
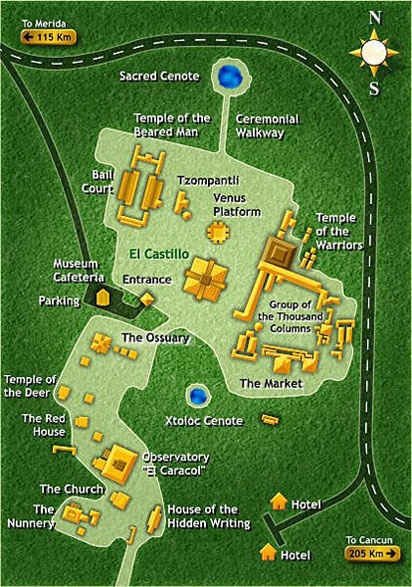
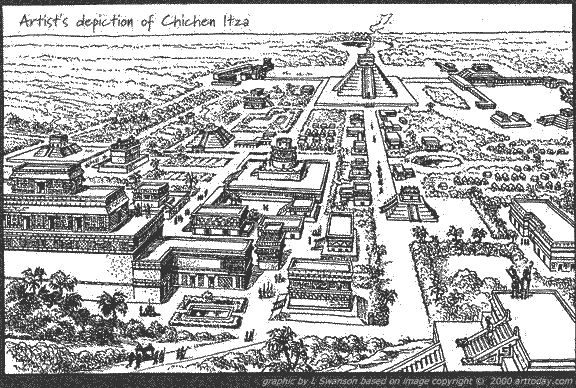
Chichen Itza, Mexico
- located in the northern lowlands
- occupied during the Classic and Post-Classic periods
- also under Toltec and Mayapan influence during the Post-Classic
period
- ceremonial center includes pyramid temples, platform temples,
platforms, seven ball courts, and three cenotes
- the most famous pyramid temple at Chichen Itza is El Castillo
(The Castle)
- El Caracol (The Shell) or The Observatory is a structure believed
to have been used for making astronomical observations
- cenotes are water-filled sinkholes with sacred attributions;
sacrifices of people and items were made in the cenotes
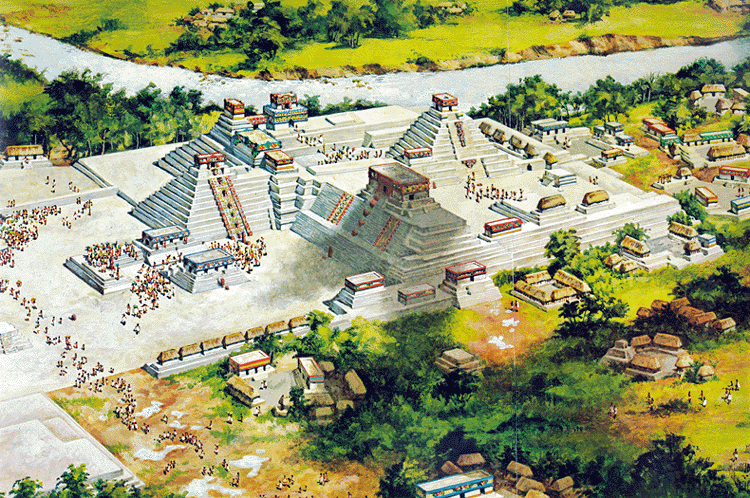
Tikal, Guatemala
- located in the southern lowlands
- most significant occupations occurred during the Classic Period
- ceremonial center included temple pyramids, two acropolii (walled
citadels with bureaucratic functions), palaces, and plazas
- ceremonial center was accessed by several causeways, or earthen
thoroughfares that rose above the surrounding lowlands
- ceremonial center was surrounded by residential areas and, beyond
the residences, agricultural fields
- the peak population of Tikal is estimated at 100,000-200,000
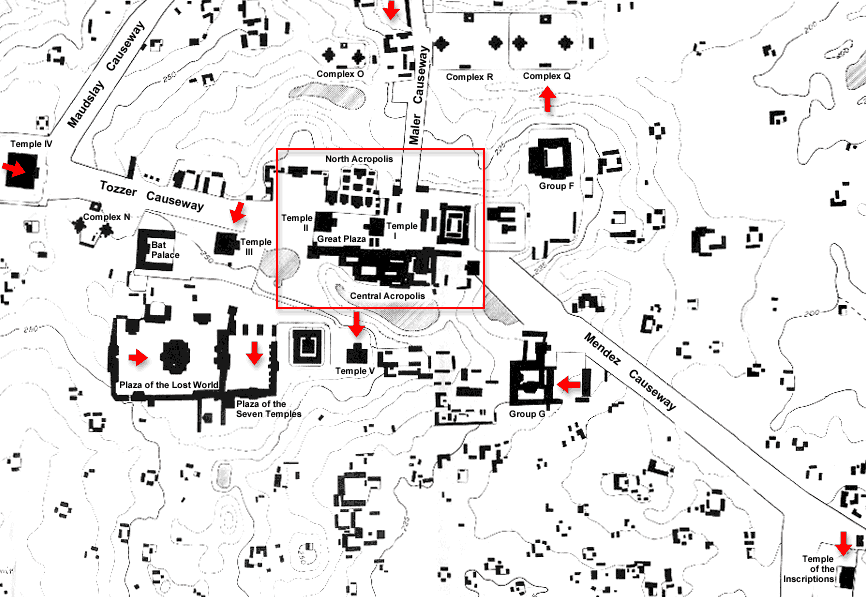
Plan View of Ceremonial Center at Tikal, Surrounded by Residences and
Causeways.
http://mayaruins.com/tikal/
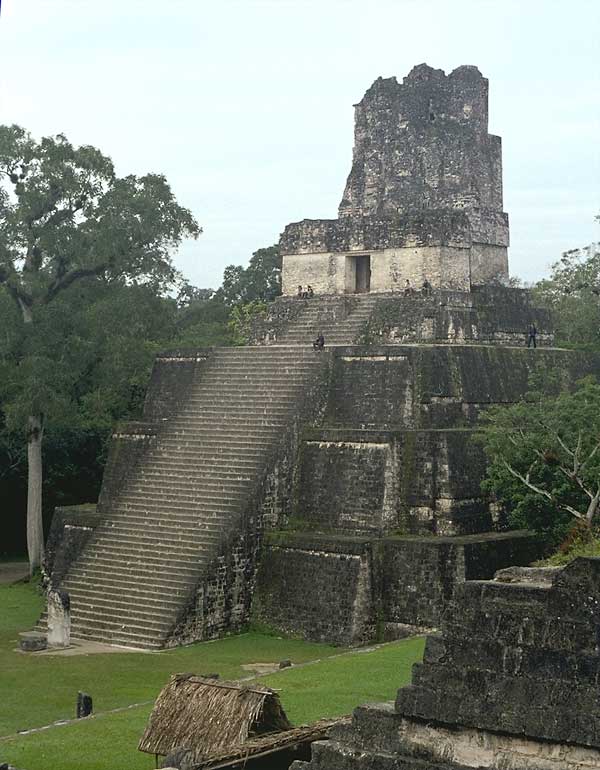

Temple II on the West Side of the Great Plaza in the Ceremonial
Center of Tikal.
Note Roof Comb on Temple at Top of Pyramid and Stela at Base of Steps.
http://mayaruins.com/tikal/
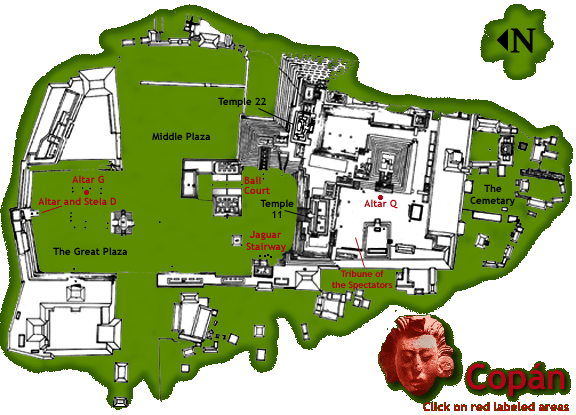
Copan, Honduras
- located in the highlands
- occupied from about AD 435 to 984
- ceremonial center included pyramid temples, ball courts,
acropoli, platforms, and plazas
- renowned for stelae with portraits of rulers and other important
individuals
- the peak population is estimated at about 20,000
other sites include El Mirador, Uaxactun, Dos Pilas, Palenque,
Yaxchilan, Uxmal, and Quiriga
POLITICAL ORGANIZATION
theocratic city-states, based on ceremonial centers
city-states arranged in polygonal pattern
power shifted between primary centers as allegiences between different
city-states changed over time
DECLINE
a variety of possible factors have been identified, including
ecological collapse, natural catastrophe, disease, cultural evolution,
invasion, internal revolt, overpopulation, or some
combination of these factors
some populations that abandoned ceremonial centers moved north into
upper Yucatan Peninsula
Return to New
World Prehistory Home Page
Visit the Western Kentucky University
Home
Page, Western Online
Page composed by Darlene Applegate, darlene.applegate@wku.edu
Last updated on November 7, 2006
All contents copyright (c), 2006. Western Kentucky
University.