
ANTH 336 New World Prehistory
Dr. Darlene Applegate
Fall 2006
Environmental Characteristics
BOUNDARIES
North: American Southwest,
West: Pacific Ocean
East: Gulf of
South: Central America culture area
Includes present-day countries of
Figure
1.
Map of
http://www.famsi.org/maps/mesomap.jpg
Figure
2.
Map of
(2) Maya Area, (3)
http://darkwing.uoregon.edu/~pyoung/CASketchMaps.html
GENERAL
ENVIRONMENTAL
CHARACTERISTICS
very diverse in vegetation, altitude, and climate
vegetation ranges from tropical forest to subtropical forest to desert
diversity led to need for cooperation between social groups in order to
get
necessary localized natural resources
primary division is highlands vs. lowlands
highlands: central portions near mountain ranges
high elevations and high relief
associated with mountain ranges and plateaus
arid to semi-arid climate
scrub vegetation
includes central and northern
lowlands:
along Pacific and
low elevations and low relief
associated with coastal zones and interior zones away from mountain ranges
semi-humid to humid climate
rainforest vegetation
includes Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico, Belize,
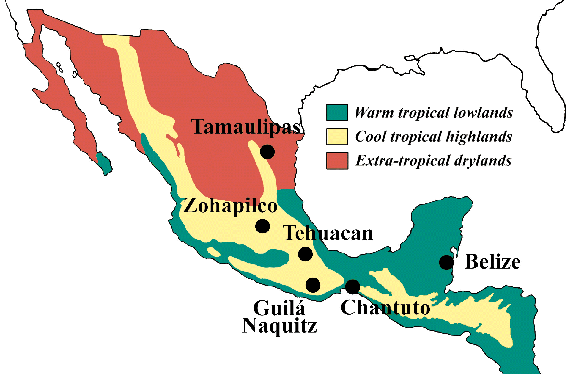
Figure
3.
Map of Major Environmental
Divisions of
Figure
4.
Map of
Archaeological Sites.
Also Note
Location of
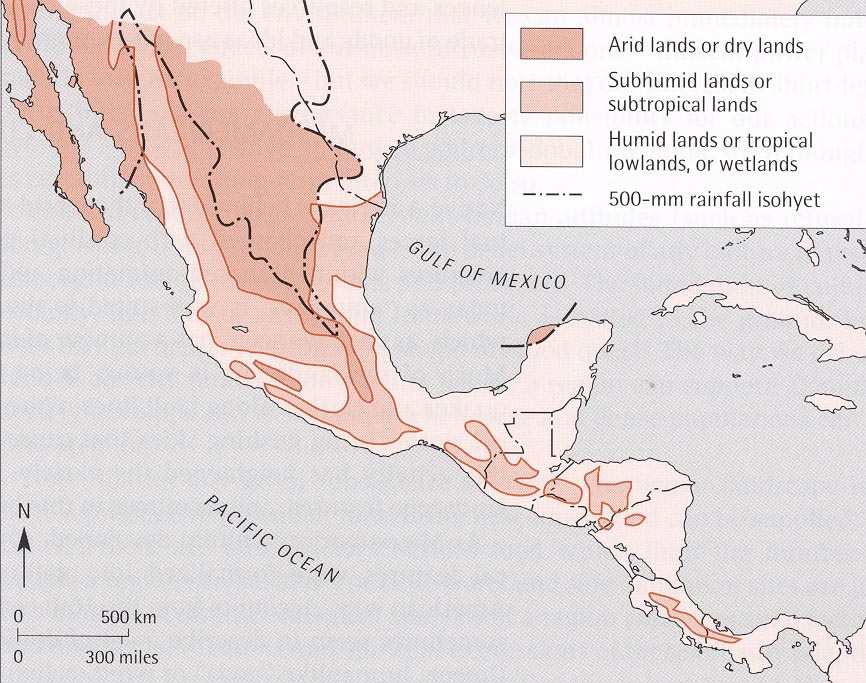
Figure
5.
Map of Environmental Zones
of

Figure
6.
Photograph of
Note Top of Pyramid
at

Figure
7.
Dry Highland Environment in
the

Figure
8.
Swampy
of the
POSITIVE FEATURES
1. availability of natural resources, including metal ores, obsidian,
clay, building
stone, salt
2. water sources including navigable rivers and lakes were available in
most
places (with some exceptions)
3. diverse faunal and floral resources
4. abundant rainfall in most places (with some exceptions)
NEGATIVE FEATURES
1. heterogeneous distribution of resources
2. poor soil in rain forest areas
3. circumscription by mountain ranges in some places and by dense
vegetation in
rain forests
4. arid (low rainfall) in some areas
5. underground drainage in karst area of
6. natural disasters:
hurricanes, mud slides, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes
Return to New World Prehistory Home Page
Visit the Western
Kentucky
University Home Page, Western Online
Page composed by Darlene Applegate, darlene.applegate@wku.edu
Last updated on November 1, 2006
All contents copyright (c), 2006.